Understanding Multi-Channel Attribution Models

Marketing attribution has evolved beyond simple last-click models into sophisticated frameworks that reflect the complex reality of modern customer journeys. Today’s consumers interact with brands across numerous touchpoints before converting, making accurate more challenging yet more crucial than ever. We’ve helped numerous businesses implement strategies that provide genuine clarity rather than misleading simplifications.
The Attribution Challenge
Most businesses face a fundamental marketing dilemma: they know half their marketing budget generates exceptional returns while the other half underperforms—but they can’t identify which half falls into each category. Multi-channel attribution models address this challenge by systematically analyzing how different touchpoints contribute to conversions.
Traditional single-touch models (like first or last click) paint incomplete pictures by assigning full credit to just one interaction. Meanwhile, customers typically engage with brands through multiple channels: seeing social ads, reading blog content, subscribing to newsletters, watching videos, and finally making purchases. Each touchpoint influences their decision, yet receives vastly different credit depending on which model you apply.
The Evolution of Attribution Thinking

Attribution modeling has transformed significantly over the past decade, evolving alongside the rapid growth of digital marketing channels and changing consumer behavior. Understanding this evolution is essential for marketers aiming to optimize campaigns and maximize ROI.
1. The Era of Last-Click Attribution
Initially, digital marketing heavily relied on last-click models, where 100% of conversion credit was given to the final touchpoint before a purchase. While administratively simple, this model often misrepresented the true customer journey, ignoring the influence of prior interactions that guided prospects toward conversion. As a result, channels like email nurturing, social media engagement, or content marketing were frequently undervalued despite their significant role in shaping customer decisions.
2. Shift to Multi-Touch Attribution
To overcome the limitations of last-click models, the industry gradually shifted toward multi-touch (MTA) models. These models distribute conversion credit across multiple touchpoints, giving marketers a more accurate understanding of how each channel contributes to customer actions. For example, a prospect may first discover a brand via a social media ad, engage with an email campaign, and finally convert through a paid search ad. Multi-touch captures this entire journey.
Research from McKinsey & Company shows that brands implementing multi-channel tracking and typically see 15–30% improvement in marketing efficiency. This gain occurs because resources can be reallocated from overvalued channels to those undervalued yet critical in driving conversions.
3. Key Multi-Touch Models and Their Impact
| Model | Description | When to Use | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Attribution | Evenly distributes credit across all touchpoints | Campaigns with multiple equally important interactions | Simple, fair, captures entire journey |
| Time-Decay Attribution | Gives more credit to touchpoints closer to conversion | Longer sales cycles | Highlights critical late-stage interactions |
| Position-Based (U-Shaped) | Assigns 40% credit to first & last touch, remaining 20% to intermediates | Awareness + conversion campaigns | Balances early discovery and final conversion impact |
| Algorithmic / Data-Driven | Uses AI to assign credit based on historical data | Complex campaigns with multiple channels | Highly accurate, optimizes budget allocation |
4. Modern Attribution and Maximizing ROI
Today, leading marketers are moving toward advanced, data-driven , integrating AI and predictive analytics to continuously optimize marketing spend across all channels. Multi-channel insights allow businesses to invest smarter, reduce wasted spend, and increase ROI significantly.
For a deeper dive into how modeling can maximize marketing ROI, see this guide: Attribution Modeling to Maximize Marketing ROI.
By understanding the evolution from simplistic last-click models to sophisticated multi-touch approaches, marketers can better capture the true value of each customer interaction, improving decision-making and overall campaign effectiveness.
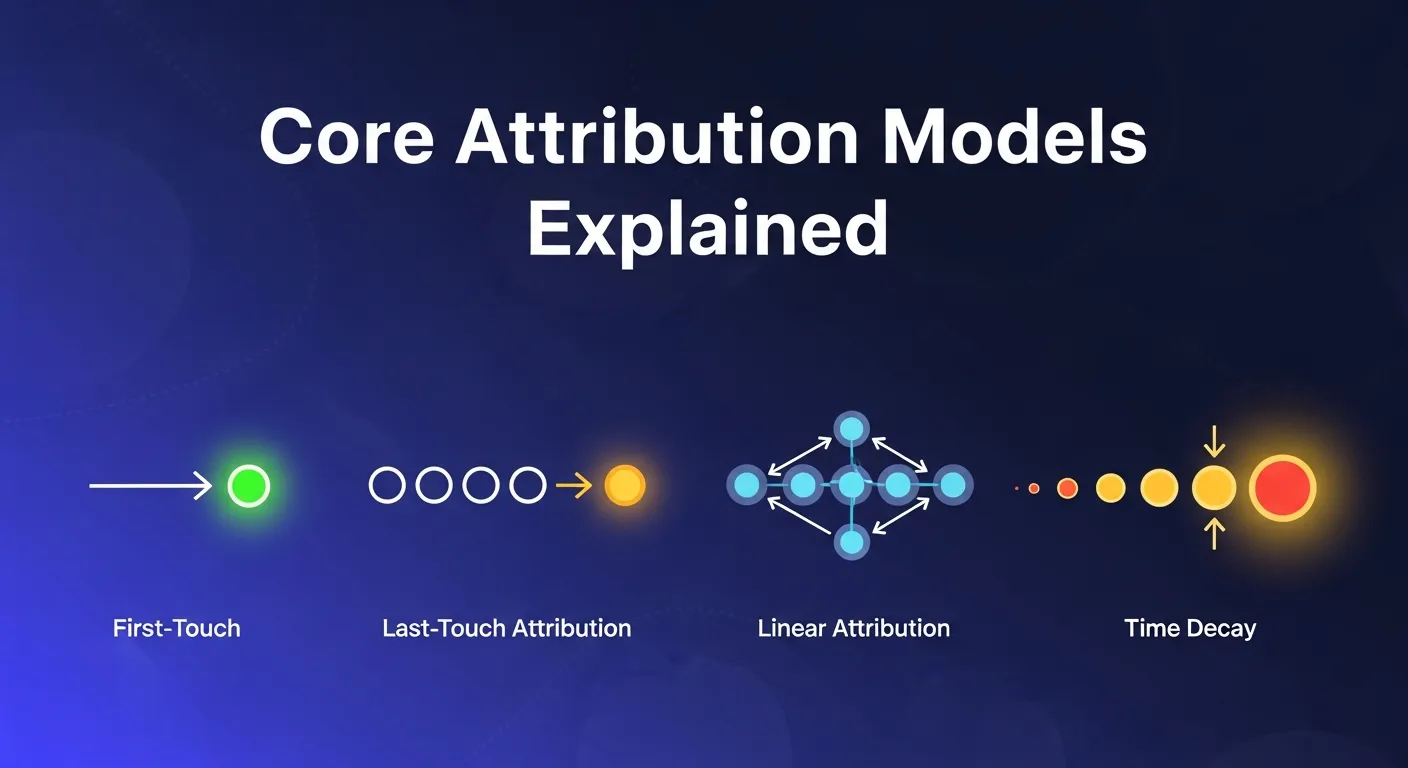
Core Attribution Models Explained
Attribution models are essential tools for understanding the effectiveness of marketing channels and campaigns. Each model offers a different lens on customer journeys, highlighting specific touchpoints while assigning credit in unique ways. Choosing the right model ensures more accurate insights and smarter resource allocation.
1. First-Touch Attribution
First-touch attribution assigns 100% of the conversion credit to the initial interaction a prospect has with your brand. This approach is valuable for identifying which channels are most effective at introducing new customers to your funnel. For example, a user discovering your brand via a social media ad or organic search would give full credit to that first encounter.
Limitation: It ignores middle- and bottom-funnel activities, such as email nurturing or retargeting ads, which are essential for converting prospects into customers.
2. Last-Touch Attribution
Last-touch gives all conversion credit to the final interaction before purchase. This model is particularly useful for understanding which channels drive immediate actions, such as direct checkout from paid search or retargeted display ads.
Limitation: It overvalues bottom-funnel activities while undervaluing channels responsible for early awareness or relationship-building.
3. Linear Attribution
Linear attribution distributes credit evenly across every touchpoint in a customer’s journey. By acknowledging all interactions, it provides a democratic view of marketing influence.
Limitation: It treats all touchpoints as equally important, failing to recognize that some interactions, like first discovery or final conversion, may contribute more significantly than others.
4. Time-Decay Attribution
Time-decay attribution assigns increasing credit to touchpoints closer to conversion, while still recognizing earlier influences. This model aligns with the idea that recent interactions often have more impact on the decision-making process. It works well for longer sales cycles, where multiple engagements build toward a conversion.
5. Position-Based (U-Shaped) Attribution
Position-based attribution, also known as U-shaped, allocates 40% of the credit each to the first and last interactions, leaving the remaining 20% to the middle touchpoints. This method balances recognition of the critical introduction and conversion moments with acknowledgment of intermediate nurturing steps like email campaigns or content downloads.
6. Algorithmic / Data-Driven Attribution
Algorithmic attribution leverages machine learning and statistical analysis to dynamically determine how much credit each touchpoint should receive. Unlike fixed-rule models, algorithmic continuously adapts based on real customer behavior data, providing highly accurate insights for complex, multi-channel campaigns.
Comparison Table of Core Attribution Models
| Model | Credit Assignment | Ideal Use Case | Strength | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Touch | 100% to first touch | Awareness campaigns | Identifies top-performing channels for new prospects | Ignores nurturing and closing interactions |
| Last-Touch | 100% to last touch | Conversion-focused campaigns | Highlights channels driving immediate conversions | Overvalues bottom-funnel activities |
| Linear | Equal credit across all touchpoints | Balanced overview | Acknowledges entire journey | Treats all touchpoints as equal |
| Time-Decay | More credit to recent touchpoints | Long sales cycles | Recognizes recency effect | Early interactions may be undervalued |
| Position-Based | 40% first & last, 20% middle | Campaigns with defined intro & close | Balances introduction and conversion | Arbitrary distribution may not fit all journeys |
| Algorithmic | Data-driven, adaptive | Complex multi-channel campaigns | Highly accurate, dynamic | Requires sufficient data & technical expertise |
For marketers interested in how traditional business principles still apply alongside modern models, this guide provides valuable insights: Why Traditional Business Models Still Drive Success.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each model, businesses can tailor their approach to accurately measure channel performance, optimize budgets, and maximize overall marketing ROI.
Implementing Practical Attribution Systems

Implementing an effective system goes beyond selecting the right model; it requires robust technical infrastructure and strategic interpretation to ensure that insights accurately reflect marketing performance. Businesses that successfully combine these elements can optimize budgets, improve campaign effectiveness, and maximize ROI.
1. Building a Solid Technical Foundation
A reliable attribution system starts with comprehensive tracking across all marketing channels. This involves:
- Unified Tagging Systems: Ensuring every touchpoint—social media, paid ads, email, website interactions—is tagged consistently for seamless data collection.
- Centralized Data Warehousing: Consolidating all marketing data in a single platform to enable cross-channel analysis.
- Integration with Analytics Tools: Linking data with CRM, marketing automation, and BI platforms for actionable insights.
Research from Gartner indicates that over 60% of marketing organizations face data integration challenges, which often hinder the ability to perform cohesive and accurate attribution analysis.
2. Defining Attribution Parameters
Beyond technical setup, systems must be thoughtfully configured to reflect true customer behavior:
- Attribution Windows: Selecting an appropriate lookback period to capture meaningful interactions without inflating the dataset with outdated touchpoints.
- Conversion Definitions: Establishing clear and consistent criteria for what counts as a meaningful conversion or engagement across channels.
- Cross-Device Tracking: Accounting for interactions across multiple devices (mobile, desktop, tablets) to avoid double-counting or gaps in the customer journey.
3. Mapping Practical Implementation Steps
| Step | Key Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Implement unified tagging & tracking across all channels | Accurate, complete dataset for analysis |
| Data Consolidation | Centralize data in a warehouse or BI tool | Enables multi-channel analysis and reporting |
| Define Metrics | Set conversion definitions & attribution windows | Ensures consistent measurement across campaigns |
| Cross-Device Mapping | Track user journeys across devices | Reduces errors, reflects true behavior |
| Analysis & Optimization | Apply chosen models and review results | Optimize budget allocation and marketing strategy |
4. Integrating Attribution with Revenue Models
Practical systems work best when connected to overall revenue frameworks, helping businesses link marketing activity directly to business outcomes. For marketers exploring this integration, this guide provides a clear explanation: Creative Market Revenue Model Explained.
By combining technical precision, thoughtful configuration, and revenue alignment, organizations can implement systems that provide actionable insights, improve decision-making, and maximize marketing ROI.
Beyond Traditional Attribution: Incrementality Testing

While traditional models are invaluable for understanding marketing touchpoints, they primarily capture correlations rather than causation. To gain a truer measure of marketing effectiveness, advanced organizations are increasingly turning to incrementality testing—experimental approaches designed to isolate the causal impact of marketing activities.
1. Understanding Incrementality Testing
Incrementality testing evaluates what would have happened without a specific marketing intervention. Unlike standard , which assigns credit based on observed interactions, incrementality testing uses controlled experiments to determine whether a campaign genuinely drove incremental conversions or merely benefited from natural customer behavior.
This approach ensures that marketing decisions are based on real impact, preventing overinvestment in channels that appear effective due to correlation alone.
2. Key Incrementality Testing Methods
Several approaches are commonly used to measure true marketing impact:
- Geo-Testing:
Marketing efforts are varied across comparable geographic regions. For example, a brand might increase ad spend in Region A while maintaining normal spend in Region B. Differences in conversion rates between regions reveal the incremental effect of the campaign. - PSA Testing (Public Service Announcement):
A control group is exposed to neutral content (such as public service announcements) instead of the branded message. Measuring the difference in conversions between the control and exposed groups establishes a baseline conversion rate, helping quantify the true lift from marketing. - Holdout Groups:
Certain qualified audience segments are intentionally excluded from specific marketing activities. By comparing conversion rates between exposed and holdout groups, marketers can directly calculate incremental impact. This method is especially useful for email campaigns, paid ads, and loyalty programs.
3. Benefits of Incrementality Testing
| Benefit | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| True Causal Insights | Identifies channels that actually drive conversions | Geo-testing shows certain paid ads caused a 12% lift |
| Budget Optimization | Prevents overinvestment in channels that appear effective | Holdout groups reveal some display ads are not driving incremental sales |
| Validation of Attribution Models | Confirms or challenges model outputs | PSA testing validates whether multi-touch attribution overvalues early touchpoints |
| Strategic Decision Making | Supports evidence-based allocation of marketing spend | Experiment results guide reallocation to highest-impact campaigns |
4. Implementing Incrementality Testing
To integrate incrementality testing into marketing strategy:
- Identify the Objective: Determine which campaigns or channels require validation.
- Design the Experiment: Select the appropriate method—geo-test, holdout, or PSA testing.
- Define Control and Test Groups: Ensure comparable audience segments for valid results.
- Measure Incremental Lift: Compare conversion rates or other KPIs between groups.
- Integrate Insights into Attribution Models: Adjust existing frameworks based on experimental findings.
5. Why Incrementality Complements Attribution
Traditional provides a map of customer touchpoints, while incrementality testing answers the question: “Which touchpoints truly drive incremental results?”
Together, these approaches offer a holistic view of marketing effectiveness—combining observational insights from attribution models with experimental validation to maximize ROI and reduce wasted spend.
By leveraging incrementality testing, marketing leaders can make decisions grounded in causal evidence, not just correlation, ensuring campaigns drive real, measurable business outcomes.
The Human Element in Attribution Analysis
While advanced technologies and sophisticated models generate rich attribution data, human judgment remains irreplaceable in turning numbers into actionable marketing insights. Attribution analysis is not just about assigning credit to touchpoints—it requires context, strategic thinking, and nuanced interpretation to drive meaningful business outcomes.
1. Why Humans Matter in Attribution
Attribution systems, even the most advanced AI-driven models, have limitations:
- They rely on historical data, which may not reflect rapidly changing consumer behavior.
- They may over- or under-value certain channels based on statistical assumptions.
- They cannot fully account for external factors such as market trends, competitor activity, or brand perception.
Skilled analysts bridge these gaps, ensuring that insights are interpreted within the broader business context. By applying critical thinking, marketers can differentiate between correlations and causation and avoid misallocating resources based on raw data alone.
2. Key Roles of Human Analysts
| Role | Responsibility | Impact on Marketing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Contextual Interpretation | Evaluates attribution findings in light of business realities and market conditions | Ensures data-driven recommendations align with strategic goals |
| Strategic Perspective | Considers long-term objectives alongside short-term conversions | Balances immediate ROI with sustainable growth |
| Data Validation | Checks for anomalies, data quality issues, or model limitations | Prevents misleading insights from driving decisions |
| Holistic Customer Understanding | Integrates qualitative knowledge (customer feedback, market trends) with quantitative data | Creates a more complete view of the customer journey |
3. Human + Technology: The Perfect Partnership
Attribution models are powerful tools, but their effectiveness increases when combined with human expertise. For example:
- Automated Attribution Models identify patterns and assign credit across multiple touchpoints.
- Human Analysts interpret these patterns, identifying actionable strategies such as reallocating budget, improving underperforming channels, or refining messaging.
Together, this partnership ensures that decision-making is both data-informed and strategically grounded, enhancing the effectiveness of campaigns and improving customer experiences.
4. Beyond Conversion Credit: Understanding Customer Journeys
Effective human-led attribution analysis goes beyond simple conversion metrics:
- Examining how different touchpoints influence brand awareness, engagement, and retention.
- Identifying gaps in the customer journey that technology alone may not highlight.
- Using insights to enhance experiences at critical touchpoints, ultimately strengthening loyalty and lifetime value.
5. Best Practices for Incorporating the Human Element
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Marketing, sales, and analytics teams should collaborate to interpret results.
- Continuous Learning: Analysts must stay updated on emerging channels, customer behavior trends, and new attribution techniques.
- Critical Review: Regularly assess attribution models against real-world performance to ensure accuracy.
- Strategic Recommendations: Translate findings into actionable strategies, not just reports.
By combining technology-driven insights with human expertise, organizations can move from numbers to nuanced understanding, making marketing decisions that are both evidence-based and strategically smart.
Integration with Marketing Strategy
Attribution insights create maximum business value when they are embedded directly into marketing strategy and budget allocation processes. Instead of being treated as a standalone reporting exercise, its should act as a strategic decision-making tool, influencing everything from campaign planning to channel investment.
1. Attribution as a Strategic Lever
Forward-thinking organizations recognize that its is more than data—it is actionable intelligence. By integrating its findings into marketing strategy, companies can:
- Optimize Campaigns in Real-Time: Adjust budgets, messaging, and targeting based on channel performance.
- Prioritize High-Impact Channels: Allocate resources to touchpoints that drive true incremental conversions.
- Forecast ROI More Accurately: Predict how changes in strategy affect revenue and customer acquisition.
In this way, transforms from a reporting metric into a continuous feedback loop that drives smarter marketing decisions.
2. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Successful integration requires breaking down silos:
- Marketing Specialists: Insights guide content creation, media buys, and campaign strategy.
- Sales Teams: Attribution informs lead prioritization and follow-up strategies.
- Finance & Analytics: Ensures budget allocation aligns with revenue impact and overall business objectives.
By sharing findings across departments, organizations foster a unified understanding of performance, enabling more productive strategic conversations and coordinated actions.
3. Benefits of Integrated Attribution
| Benefit | How It Works | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Informed Budget Allocation | Adjust investments based on measured impact across channels | Increasing spend on high-performing paid search campaigns while reducing underperforming display ads |
| Enhanced Campaign Optimization | Real-time feedback guides creative, messaging, and channel adjustments | Refining email sequences based on multi-touch attribution data |
| Shared Performance Language | Teams operate with a consistent framework for evaluating success | Marketing, sales, and finance align on what counts as a conversion or KPI |
| Strategic Agility | Quick insights allow faster response to market changes | Shifting resources to channels driving incremental conversions during peak seasons |
| Improved ROI Measurement | Connects marketing activity directly to business outcomes | Predicting revenue lift from multi-channel campaigns and re-allocating resources accordingly |
4. Best Practices for Seamless Integration
- Standardize Frameworks: Align models, KPIs, and conversion definitions across all teams to ensure consistent measurement and shared understanding.
- Establish Feedback Loops: Continuously feed performance insights into campaign planning, optimization, and budget allocation for dynamic decision-making.
- Promote Data Transparency: Make results accessible to all stakeholders, enabling informed decisions and fostering collaboration across departments.
- Integrate Quantitative & Qualitative Insights: Combine performance data with customer feedback, market trends, and competitive intelligence to form a holistic strategy.
- Monitor and Iterate: Regularly review metrics, test assumptions, and refine processes to maintain accuracy and adapt to evolving customer behavior.
5. The Strategic Advantage
Organizations that fully integrate attribution insights into their marketing strategy gain a competitive edge. By turning attribution from a passive report into active guidance, marketers can:
- Make smarter budget decisions
- Improve campaign performance
- Align teams on shared goals
- Drive measurable business growth
In essence, integrated attribution transforms marketing from reactive execution into proactive strategy, enabling organizations to continuously maximize ROI while understanding the true drivers of customer behavior.
Marketing Maturity and Measurement Sophistication
Marketing measurement sophistication typically evolves alongside broader organizational maturity. Companies generally progress through several developmental stages:
- Channel-Specific Reporting: Early-stage organizations track performance in silos, focusing on individual channels without connecting the broader customer journey.
- Basic Multi-Touch Tracking: Organizations begin unifying conversion tracking across multiple channels, providing a clearer view of how various touchpoints contribute to outcomes.
- Algorithmic Models: With more data and technical capabilities, companies adopt machine learning to dynamically evaluate channel performance and optimize campaigns.
- Integrated Systems: Mature organizations combine advanced modeling with controlled experiments and unified customer journey analytics, enabling a holistic view of marketing effectiveness.
Each stage requires approaches aligned with available data, technical capabilities, and organizational readiness. Attempting highly complex modeling before establishing foundational measurement practices can create confusion, misallocation of resources, and inaccurate insights.
The Future of Marketing Measurement
Measurement continues evolving toward more sophisticated, customer-centric approaches. Emerging trends include:
- Privacy-First Solutions: Adapting to cookie deprecation, increasing privacy regulations, and shifting consumer expectations.
- Enhanced Cross-Device and Online-to-Offline Tracking: Capturing interactions across multiple platforms and offline touchpoints for a complete customer journey view.
- Integration with Customer Experience Metrics: Combining performance measurement with broader experience insights to optimize engagement and loyalty.
- Machine Learning Optimization: Continuously refining models to reflect changing behavior patterns, ensuring campaigns remain effective in complex, multi-channel environments.
These developments will help marketers maintain accurate, actionable insights despite increasingly complex customer journeys that span numerous devices, channels, and environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between inbound and outbound product marketing?
Inbound marketing focuses on attracting customers through content, SEO, and organic engagement, while outbound marketing proactively reaches audiences via ads, emails, and direct campaigns. For a detailed comparison, see Inbound vs Outbound Product Marketing.
2. How can outbound marketing help promote a new product effectively?
Outbound marketing enables brands to directly reach target audiences using channels like email campaigns, social media ads, and display networks, accelerating product awareness and adoption. Learn more about this approach here: Outbound Marketing for Product Promotion.
3. What is a product promotion funnel in outbound marketing?
A product promotion funnel outlines the stages a prospect moves through—from awareness to consideration to conversion—while using outbound strategies such as targeted campaigns and retargeting. See an in-depth guide: Product Promotion Funnel & Outbound Marketing.
4. Why is multi-touch marketing measurement important for campaign success?
Multi-touch measurement captures the influence of all touchpoints in a customer journey, rather than overvaluing the first or last interaction. This ensures better budget allocation, higher ROI, and data-driven campaign optimization.
5. How do machine learning models improve marketing measurement?
Machine learning dynamically analyzes historical and real-time data to assign credit to channels based on actual performance. This allows organizations to identify high-impact touchpoints and optimize marketing spend continuously.
6. What role do holdout groups play in evaluating marketing effectiveness?
Holdout groups involve intentionally excluding certain segments from campaigns to measure the incremental impact of marketing activities. This helps determine which channels truly drive conversions versus those with only correlational influence.
7. How can marketing teams integrate measurement insights into strategy?
Teams can integrate insights by standardizing KPIs, establishing feedback loops, promoting data transparency, and combining quantitative and qualitative data for a holistic view of performance.
8. How does privacy-first measurement impact marketing strategy?
With evolving privacy regulations and the deprecation of cookies, privacy-first measurement ensures marketers can track performance responsibly while maintaining accuracy and compliance across channels.
9. What is the importance of cross-device tracking in modern marketing?
Customers interact across multiple devices—mobile, desktop, and offline touchpoints. Cross-device tracking ensures complete visibility into the journey, preventing data gaps and improving the accuracy of performance evaluation.
10. How can organizations mature their marketing measurement practices?
Marketing maturity progresses from channel-specific reporting to unified, algorithmic, and experimental models. Organizations should align sophistication with data availability, technical capabilities, and strategic readiness to avoid confusion and maximize ROI.