B2B vs. B2C Outbound Marketing: What’s the Difference?

B2B vs B2C outbound marketing represents two distinct approaches to reaching and converting audiences. Outbound marketing is a foundational strategy for reaching new customers. By proactively sending your message out to a broad audience, you can generate awareness and drive sales. However, the approach you take depends heavily on who you’re trying to reach. Marketing to another business (B2B) requires a different playbook than marketing directly to a consumer (B2C).
Understanding the distinctions between B2B and B2C outbound marketing is crucial for any business owner or marketer. A B2C strategy applied to a B2B audience will likely fall flat, wasting time and resources. Conversely, a B2B approach might feel too formal and detached for individual consumers. This guide will break down the key differences, explore effective strategies for each, and help you determine the best path for your business. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to tailor your outbound efforts for maximum impact, whether you’re selling to a boardroom or a living room.
What is Outbound Marketing?

Before we compare B2B vs B2C approaches, let’s solidify our understanding of outbound marketing. Outbound marketing involves actively pushing a marketing message out to potential customers. Think of it as the marketer initiating the conversation. This contrasts with inbound marketing, where customers find you through content like blog posts or search engine results.
Common outbound marketing tactics include:
- Email marketing (cold outreach)
- Direct mail
- Cold calling
- Trade shows and events
- Print, television, and radio advertising
- Digital ads (like social media ads and paid search)
While some consider digital ads to be inbound, they function as outbound when they interrupt a user’s experience to present a marketing message, rather than being sought out. The core idea of outbound—whether in B2B vs B2C contexts—is to cast a wide net to capture attention and generate leads.
Key Differences Between B2B and B2C Audiences
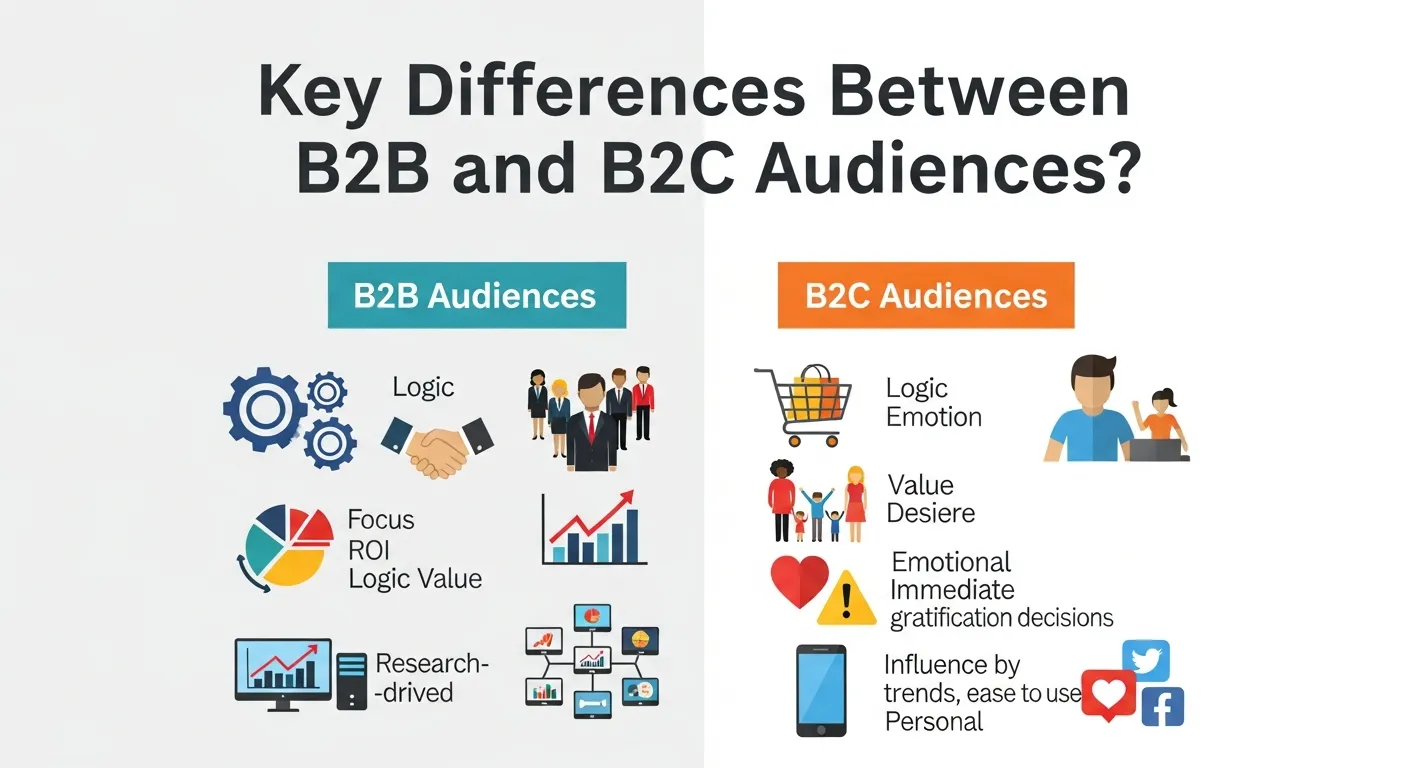
The fundamental differences between B2B and B2C outbound marketing stem from the distinct characteristics of their target audiences. These differences influence everything from your messaging and channel selection to the length of your sales cycle.
1. The Decision-Making Process
B2C: The B2C customer is typically an individual making a purchase for personal use. Their decision-making process is often driven by emotion, immediate needs, or desires. While logic plays a part (especially for larger purchases), the buying journey is usually short and straightforward. A consumer might see an ad for a new pair of sneakers and buy them within minutes. The decision-maker is the end-user, and they answer only to themselves.
B2B: In the B2B vs B2C context, the buying process is far more complex. A purchase decision rarely rests on a single person. Instead, it involves multiple stakeholders across different departments, each with their own priorities and concerns. This group, often called a buying committee, might include:
- The Initiator: The person who first identifies a need.
- The Influencer: Someone whose opinion sways the decision (e.g., an IT specialist).
- The Decider: The person with the authority to make the final choice (e.g., a department head).
- The Buyer: The individual who handles the logistics of the purchase (e.g., a procurement officer).
- The End-User: The person or team who will actually use the product or service.
Because of this complexity, B2B decisions are heavily based on logic, return on investment (ROI), efficiency gains, and long-term value. The sales cycle can stretch from weeks to months, or even years.
2. Relationship and Trust
When comparing B2B vs B2C relationships, the biggest distinction lies in how trust and connection are built between brands and their audiences.
B2C: In the B2C landscape, relationships are often transactional. While brand loyalty is a goal, the initial focus is usually on making a single sale. Trust is built through social proof such as reviews, celebrity endorsements, and brand reputation. The relationship is typically with the brand as a whole, rather than a specific person.
B2B: In contrast, B2B marketing is centered around building long-term, consultative relationships. The purchase is often the beginning—not the end—of the partnership. Trust is established through expertise, reliability, and a deep understanding of the client’s business challenges. A dedicated account manager or sales representative often becomes the face of the company, serving as a trusted advisor and maintaining consistent communication over time.
3. Messaging and Tone
B2C: B2C messaging is designed to be simple, emotionally resonant, and benefit-driven. It focuses on how the product will make the customer’s life better, easier, or more enjoyable. The language is often casual, entertaining, and aims to create an immediate connection. Humor, storytelling, and aspirational content are common.
B2B: B2B messaging is professional, informative, and value-oriented. It speaks to business challenges and offers concrete solutions. The tone is authoritative and educational, highlighting ROI, efficiency, and competitive advantage. The content is packed with data, case studies, and industry-specific language. In B2B vs B2C marketing, you’re not selling a product; you’re selling a solution to a business problem.
4. Purchase Motivation
B2C: Consumers are motivated by personal needs, wants, and status. They buy things to solve a personal problem (a warmer coat for winter), for entertainment (a video game), or to express their identity (a luxury watch).
B2B: Businesses are motivated by logic and financial sense. They invest in products or services to increase revenue, decrease costs, improve productivity, or mitigate risk. The ultimate goal is to improve the bottom line. A B2B purchase is an investment, and it must be justified with a clear business case.
Effective B2B Outbound Marketing Strategies

When comparing B2B vs B2C approaches, one of the biggest differences lies in strategy. While B2C outbound marketing focuses on emotion and scale, B2B outbound marketing relies on precision, personalization, and long-term relationship building. Below are the most effective B2B strategies designed to reach decision-makers and drive results.
1. Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
ABM is a highly focused strategy where marketing and sales teams work together to target a select group of high-value accounts. Instead of casting a wide net, you treat each target company as a market of one.
How it works: Identify key companies that perfectly fit your product or service. Then, craft highly personalized campaigns and content specifically for stakeholders within those companies.
Channels:
- LinkedIn ads targeted by job title and company
- Personalized cold emails
- Direct mail with custom packages
- Exclusive webinars or invite-only events
Why it works for B2B: ABM directly addresses the complex buying committee by engaging multiple decision-makers with tailored messaging, building consensus, and accelerating the sales cycle.
2. Strategic Cold Emailing
Unlike broad consumer campaigns, B2B cold emailing focuses on quality over quantity. It’s about sending a well-researched, personalized message to the right decision-maker rather than mass emailing thousands of contacts.
How it works: Research your prospect’s company, role, and recent activities. Reference a specific pain point they likely face and show how your solution can help. The goal isn’t to sell immediately but to start a meaningful conversation.
Best Practices:
- Subject Line: Make it specific and intriguing (e.g., Idea for improving [Company Name]’s lead gen).
- Personalization: Mention a recent achievement or shared connection.
- Value Proposition: Clearly outline the benefit.
- CTA: Ask for a short, low-commitment call.
3. LinkedIn Outreach
LinkedIn is the premier social platform for B2B professionals, making it a cornerstone of outbound efforts.
How it works: Use LinkedIn Sales Navigator to identify ideal prospects by role, industry, and company size. Send personalized connection requests and InMail messages that highlight how your product or service can provide value.
Why it works for B2B: It enables precise targeting and builds professional credibility. Unlike B2B vs B2C social outreach, where B2C relies on emotion and visuals, B2B LinkedIn campaigns focus on logic and ROI-driven conversations.
4. Trade Shows and Industry Events
Even in a digital-first world, face-to-face engagement remains one of the most powerful tools in B2B outbound marketing.
How it works: Secure a booth at key trade shows or sponsor relevant industry conferences. Demonstrate your product, network with potential clients, and showcase your brand’s expertise.
Why it works for B2B: These events bring together a highly targeted audience of decision-makers. Unlike B2B vs B2C events, which focus on product experience and entertainment, B2B trade shows emphasize networking, trust-building, and knowledge sharing.
Effective B2C Outbound Marketing Strategies
B2C outbound marketing needs to be broad, engaging, and emotionally appealing to capture the attention of individual consumers in a crowded marketplace. When comparing B2B vs B2C strategies, it’s clear that B2C relies more on emotional appeal and mass reach, while B2B focuses on logic and relationship-building.
1. Social Media Advertising
Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok offer powerful targeting tools that allow you to reach consumers based on their interests, demographics, and online behaviors. When it comes to B2B vs B2C outbound marketing, social media plays a much larger role in B2C campaigns due to its emotional and visual appeal.
How it works: Create visually compelling ads—such as videos, carousels, or stories—that showcase your product in an aspirational or problem-solving context. Use clear CTAs like “Shop Now” or “Learn More” to drive immediate action. Here’s more info about social media services.
Unlike B2B marketing, where decision-making is logical and relationship-driven, B2B vs B2C strategies on social media highlight how B2C brands connect instantly with audiences through creativity and storytelling.
Why it works for B2C: You can reach millions of potential customers where they spend their free time. The emotional and visual nature of social media is ideal for B2C messaging and clearly demonstrates the difference between B2B vs B2C communication styles—B2B thrives on data and precision, while B2C succeeds through emotion and engagement.
2. Influencer Marketing
Collaborating with influencers allows you to tap into a pre-built community of trust.
How it works: Partner with influencers whose audience aligns with your target customer. They can promote your product through sponsored posts, stories, or videos. An authentic recommendation from a trusted influencer can feel more like a friendly suggestion than an ad.
In the B2B vs B2C marketing landscape, influencer collaborations can take different forms. For B2C, it often means working with lifestyle, fashion, or entertainment influencers who can drive immediate engagement and impulse purchases. For B2B, influencer marketing may involve industry experts, thought leaders, or niche creators who can build credibility and educate potential clients.
Why it works for B2C: Consumers trust recommendations from people they follow. In the B2B vs B2C context, this trust dynamic highlights the emotional appeal of B2C marketing, where social proof and relatability can drive awareness and sales very quickly.
3. Email Marketing Promotions
Unlike B2B cold emailing, B2C email marketing is often geared toward a subscriber list you’ve already built. However, outbound-style promotions can be used to re-engage lapsed customers or push a major sale.
How it works: Send out broadcast emails announcing flash sales, new product drops, or special holiday promotions. The messaging should be urgent and exciting, creating a sense of FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out).
Why it works for B2C: It drives immediate, measurable sales. The direct call to action and time-sensitive nature of the offer encourage impulse buys.
4. Traditional Media (with a Modern Twist)
While TV, radio, and print ads may seem old-fashioned, these traditional media can still be effective for reaching a broad B2C audience.
How it works: For brands with a large budget, a Super Bowl commercial or a full-page ad in a popular magazine can generate massive awareness. To modernize this approach, integrate a digital element, like a QR code that leads to a special online offer or a unique hashtag to encourage social media conversation.
Why it works for B2C: These channels excel at mass-market brand building and reaching demographics that may not be as active online. Compared to B2B vs B2C strategies, B2C traditional media focuses more on emotional engagement, while B2B prioritizes thought leadership and professional credibility.
Your Path to Outbound Success
B2B vs B2C outbound marketing isn’t about deciding which is “better” — it’s about deeply understanding your audience and aligning your tactics with their motivations, behaviors, and decision-making processes.
In B2B outbound marketing, success lies in a targeted, value-driven, and relational approach. Focus on building trust and demonstrating clear ROI through strategies like Account-Based Marketing, personalized email sequences, and LinkedIn outreach that speak directly to business decision-makers. Focus on building trust and demonstrating clear ROI with strategies like Account-Based Marketing and personalized LinkedIn outreach.
In contrast, B2C outbound marketing is all about capturing attention and creating emotional connections at scale. Leverage the power of social media advertising, influencer collaborations, and limited-time promotions to inspire immediate action and brand loyalty.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of B2B vs B2C marketing ensures your outbound efforts are thoughtful and customer-centric. By moving beyond a one-size-fits-all strategy and tailoring your message to the right audience on the right channels, you can transform outbound marketing into a powerful engine for sustainable growth.
FAQ: B2B vs B2C Outbound Marketing
1. What does B2B vs B2C mean in marketing?
B2B (Business-to-Business) marketing targets other companies, while B2C (Business-to-Consumer) marketing focuses on individual consumers. The difference lies in the audience, messaging, and sales process.
2. What is the main difference between B2B vs B2C outbound marketing?
The main difference is in approach—B2B outbound marketing emphasizes logic, ROI, and long-term relationships, while B2C focuses on emotion, convenience, and quick decision-making.
3. Why is understanding B2B vs B2C important for marketers?
Understanding B2B vs B2C helps marketers craft the right tone, messaging, and strategies for their target audience, leading to better engagement and conversion rates.
4. Which channels work best for B2B outbound marketing?
Effective B2B channels include LinkedIn outreach, account-based marketing, personalized cold emails, and trade shows, all of which help build relationships with decision-makers.
5. Which channels are most effective for B2C outbound marketing?
For B2C, social media advertising, influencer marketing, and promotional email campaigns are the most effective channels to reach and engage consumers quickly.
6. Is outbound marketing still effective for B2B and B2C?
Yes. Despite the rise of inbound marketing, outbound marketing remains effective for both B2B and B2C when done strategically with targeted messaging and data-driven campaigns.
7. How long is the sales cycle in B2B vs B2C marketing?
B2B sales cycles are longer due to multiple decision-makers and complex approval processes. B2C sales cycles are typically short, with many purchases made on impulse or emotion.
8. How does messaging differ between B2B vs B2C marketing?
B2B messaging is professional and focused on value and ROI, while B2C messaging is emotional, engaging, and designed to capture attention quickly.
9. Can a business use both B2B and B2C outbound marketing?
Absolutely. Some businesses serve both audiences and adapt their outbound strategies accordingly, using different tones, channels, and offers for each segment.
10. Which is more cost-effective: B2B or B2C outbound marketing?
It depends on your goals. B2B outbound marketing often costs more per lead but results in higher-value clients. B2C outbound marketing can be less expensive per contact but relies on high-volume sales.
Learn more about: SaaS Outbound Marketing Playbook: From Cold to Closed